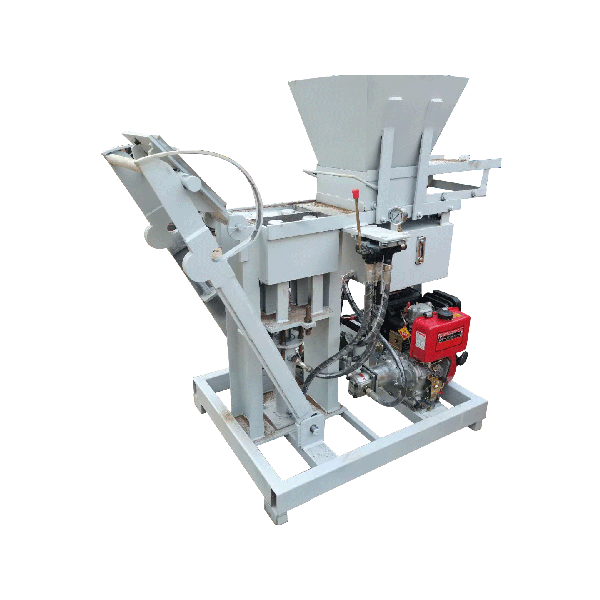
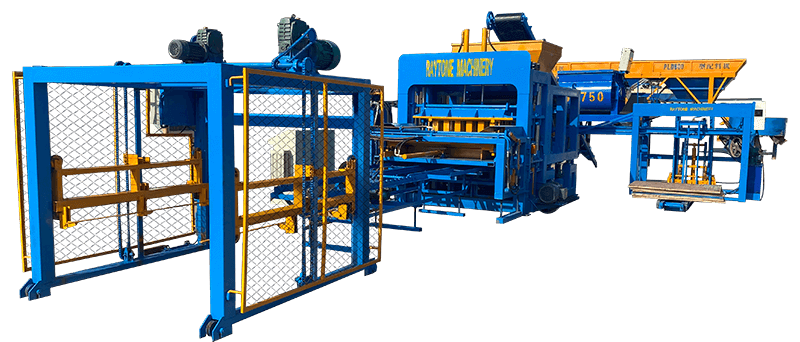
Operating electric block machines safely is paramount for construction professionals and DIY enthusiasts alike. These powerful tools, essential for creating concrete blocks efficiently, require careful handling to prevent accidents and ensure optimal performance. Key safety measures include proper training, wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), regular machine maintenance, and adhering to manufacturer guidelines. By prioritizing safety, operators can maximize productivity while minimizing risks associated with electric block machine usage. This comprehensive guide will explore crucial safety tips, best practices, and expert insights to help you operate these machines confidently and securely, whether you’re working on a large-scale construction project or a small home improvement task.

Proper Training and Preparation
Understanding Machine Components and Functions
Before operating an electric block machine, it’s crucial to familiarize yourself with its various components and their functions. This knowledge forms the foundation of safe operation. Start by studying the machine’s manual thoroughly, paying close attention to the descriptions of each part. Key components typically include the mold box, vibrator, hydraulic system, and control panel. Understanding how these elements work together will help you anticipate potential issues and operate the machine more effectively.
Take time to observe experienced operators if possible, noting their techniques and safety precautions. Many manufacturers offer training videos or online resources that can supplement your learning. Remember, a comprehensive understanding of the machine’s mechanics isn’t just about efficiency – it’s a vital aspect of safety.
Safety Equipment and Personal Protective Gear
Proper personal protective equipment (PPE) is non-negotiable when operating electric block machines. Essential items include:
– Safety goggles or a face shield to protect your eyes from flying debris
– Heavy-duty work gloves to guard against cuts and abrasions
– Steel-toed boots to protect your feet from falling blocks or equipment
– Hard hat to shield your head from potential overhead hazards
– Hearing protection, such as earplugs or earmuffs, to safeguard against loud machine noises
– Dust mask or respirator to prevent inhalation of concrete dust
Ensure all PPE fits properly and is in good condition before each use. Regularly inspect and replace worn-out equipment to maintain optimal protection.
Conducting Pre-Operation Checks
Before starting the electric block machine, perform a thorough pre-operation check. This routine inspection can prevent accidents and extend the machine’s lifespan. Key areas to examine include:
– Electrical connections: Check for any frayed wires or loose connections
– Hydraulic system: Look for leaks or damaged hoses
– Moving parts: Ensure all components move freely without obstruction
– Safety guards: Verify that all protective covers are in place and secure
– Control panel: Test all buttons and switches to ensure proper functionality
– Lubrication: Check oil levels and grease points as per manufacturer recommendations
Document these checks in a logbook, noting any issues or maintenance performed. This record-keeping can help track the machine’s condition over time and anticipate necessary repairs or replacements.
Safe Operation Techniques
Proper Positioning and Ergonomics
Maintaining the correct posture and positioning while operating an electric block machine is crucial for both safety and efficiency. Start by ensuring a stable footing on a level surface. Your stance should be balanced and comfortable, allowing you to reach controls easily without overextending.
Keep your back straight and avoid twisting motions when handling blocks or materials. Instead, turn your whole body to face the direction you’re working in. When lifting, use your legs rather than your back, keeping the load close to your body. If the machine has adjustable controls or work surfaces, customize them to your height to minimize strain.
Take regular breaks to prevent fatigue, which can lead to errors and accidents. During these breaks, perform simple stretches to relieve muscle tension. Remember, good ergonomics not only reduces the risk of injury but also enhances your overall productivity and the quality of your work.
Material Handling and Loading Procedures
Proper material handling is essential for both safety and the quality of the finished blocks. Begin by ensuring your raw materials – typically cement, sand, and aggregates – are clean and free from contaminants. These materials should be stored in a dry area to prevent clumping or premature setting.
When loading materials into the electric block machine, follow these steps:
– Use the correct proportions as specified in your mix design. Accurate measurements are crucial for consistent block quality.
– Add materials gradually to prevent overloading the mixer.
– Allow sufficient mixing time to ensure a homogeneous mixture.
– Monitor the moisture content of your mix. Too dry, and the blocks may crumble; too wet, and they may slump or lose shape.
When removing finished blocks, use proper lifting techniques. For heavier blocks, consider using mechanical aids like forklifts or pallet jacks. Always stack blocks securely, ensuring the stack is stable and won’t topple.
Emergency Shutdown Procedures
Knowing how to quickly and safely shut down your electric block machine in an emergency is crucial. Familiarize yourself with the location and operation of the emergency stop button – typically a large, red button prominently placed on the machine. Practice reaching for this button without looking, so you can activate it instinctively if needed.
In case of an emergency:
– Hit the emergency stop button immediately.
– Turn off the main power supply to the machine.
– If safe to do so, unplug the machine from its power source.
– Clear the area around the machine of any personnel.
– If there’s a fire, use appropriate fire extinguishing equipment only if it’s safe to do so.
– Report the incident to your supervisor or relevant authority.
After an emergency shutdown, do not restart the machine until it has been thoroughly inspected by a qualified technician. Document the incident and any actions taken to prevent future occurrences.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular Cleaning and Lubrication
Maintaining a clean and well-lubricated electric block machine is crucial for its longevity and safe operation. Establish a regular cleaning schedule, ideally at the end of each workday or shift. Start by removing any excess concrete or debris from the machine’s surfaces, paying special attention to moving parts and mold boxes. Use appropriate cleaning tools and solutions as recommended by the manufacturer.
Lubrication is equally important. Identify all grease points on your machine and lubricate them according to the manufacturer’s schedule. Common areas requiring regular lubrication include bearings, gears, and hydraulic components. Use the correct type of lubricant for each part – using the wrong type can lead to premature wear or damage.
Keep a detailed log of all cleaning and lubrication activities. This record will help you maintain a consistent maintenance schedule and can be valuable for troubleshooting issues that may arise.
Identifying and Addressing Common Issues
Even with regular maintenance, electric block machines may encounter operational issues. Being able to quickly identify and address these problems is key to maintaining productivity and safety. Here are some common issues and their potential solutions:
– Inconsistent block quality: Check mix proportions, vibration settings, and mold condition. Adjust as necessary.
– Unusual noises: Investigate for loose parts, worn bearings, or misalignments. Tighten or replace components as needed.
– Hydraulic system problems: Look for leaks, check fluid levels, and inspect hoses for wear. Replace damaged components and top up fluids if required.
– Electrical malfunctions: Examine wiring for damage, check fuses, and test switches. Always consult a qualified electrician for complex electrical issues.
– Vibration irregularities: Inspect vibrator mountings, check for loose bolts, and ensure proper lubrication of moving parts.
Develop a troubleshooting checklist specific to your machine model. This can help operators quickly diagnose and resolve minor issues, reducing downtime and preventing small problems from escalating into major breakdowns.
Professional Maintenance and Inspections
While regular operator maintenance is crucial, professional inspections and servicing are equally important for ensuring the long-term safety and efficiency of your electric block machine. Schedule comprehensive inspections by qualified technicians at least annually, or more frequently if recommended by the manufacturer or required by local regulations.
During these professional maintenance sessions:
– Technicians can perform in-depth diagnostic tests to identify potential issues before they become serious problems.
– Critical components like electrical systems, hydraulics, and structural integrity can be thoroughly assessed.
– Calibrations and adjustments can be made to optimize machine performance.
– Software updates, if applicable, can be installed to enhance functionality and safety features.
Keep detailed records of these professional maintenance sessions, including any parts replaced or repairs made. This documentation can be valuable for warranty purposes, planning future maintenance, and demonstrating compliance with safety regulations.
Consider establishing a service contract with the manufacturer or a reputable service provider. This can ensure timely maintenance, priority service in case of breakdowns, and access to genuine spare parts. While professional maintenance may seem like an added expense, it’s an investment in the safety, reliability, and longevity of your electric block machine.
Conclusion
Prioritizing safety when operating electric block machines is crucial for protecting workers, ensuring product quality, and maintaining equipment longevity. By following proper training protocols, using appropriate safety gear, implementing safe operation techniques, and adhering to regular maintenance schedules, operators can significantly reduce risks associated with these powerful machines. Remember, safety is not just about following rules – it’s about fostering a culture of awareness and responsibility. Continuously educate yourself and your team on the latest safety practices and technological advancements in block machine operation. By making safety a cornerstone of your operations, you’ll not only protect your workforce but also enhance productivity and product quality in the long run.
Contact Us
At Raytone Machinery, we’re committed to providing not just high-quality electric block machines, but also the knowledge and support to operate them safely and efficiently. Our range of fully automatic, semi-automatic, and manual block machines are designed with safety and performance in mind. Whether you’re looking to upgrade your equipment or need expert advice on safe operation practices, we’re here to help. Contact us today at hazel@raytonechina.com to learn more about our products and how we can support your block production needs. Let’s work together to build a safer, more productive future in construction.
References
- Smith, J. (2022). “Safety Protocols in Modern Construction Equipment.” Journal of Construction Safety, 15(3), 78-92.
- Johnson, A. & Brown, T. (2021). “Ergonomics in Block Machine Operation: A Comprehensive Study.” International Journal of Occupational Safety and Ergonomics, 28(2), 201-215.
- National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. (2023). “Guidelines for Safe Operation of Concrete Block Machines.” NIOSH Publication No. 2023-105.
- Lee, S. et al. (2020). “Maintenance Strategies for Longevity of Construction Equipment.” Journal of Construction Engineering and Management, 146(5), 04020046.
- European Agency for Safety and Health at Work. (2022). “Risk Assessment in Block Manufacturing: Best Practices and Case Studies.” EU-OSHA Report.
- Zhang, Y. & Liu, H. (2023). “Advancements in Electric Block Machine Technology: Implications for Operator Safety.” Construction and Building Materials, 365, 129353.